Noise Type
\[\overline{v_n^2}/ \Delta f = 4 k T R, \quad \overline{i_n^2} / \Delta f = \frac{4kT}{R}\]
- MOSFET channel is (non-uniform) resistor
\[\overline{i_n^2}/\Delta f = 4 kT \gamma g_{d0}\] \[g_{do} = \frac{\partial I_{D}}{\partial V_{DS}} \Bigg|_{V_{DS}=0}\]
\[\overline{i_n^2} /\Delta f = 2 q I_{DC}\]
\[\overline{v_n^2} / \Delta f = \frac{K}{C_{ox}WL} \cdot \frac{1}{f}\]
- Flicker noise doesn’t depend on bias current or temperature (really?). PMOS typically has smaller flicker noise than NMOS.
- Larger device (larger \(WL\)) will have smaller flicker noise.
Output Noise
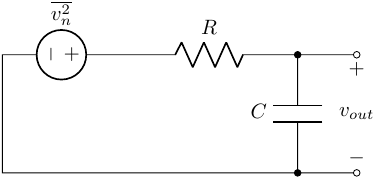
Example 01
![example-01]() Example 01
Example 01
\[\begin{align} \overline{v_{out}^2}/\Delta f &= 4kTR \Big|\frac{1}{1+j2\pi f RC}\Big|^2 \end{align}\] \[\begin{align} \overline{v_{out}^2}=&\int_{0}^{\infty} \Big| \frac{1}{1 + j2\pi f RC} \Big|^2 4 kT R d f = 4 k T R \int_{0}^{\infty} \frac{1}{1 + (2 \pi R C f)^2} df \\ = & \frac{4 k T R}{2 \pi RC}\int_{0}^{\infty} \frac{2 \pi R C}{1 + (2\pi R C f)^2}df\\ =& \frac{2 kT}{\pi C} \int_{0}^{\infty}\frac{1}{1+x^2}dx\\ =& \frac{2 kT}{\pi C} \frac{\pi}{2} = \frac{kT}{C} \end{align}\]
the calculation can be viewed as, using the cutoff frequency \(f_c = \frac{1}{2\pi RC}\) of \(H(s) = \frac{1}{1 + sRC}\)
\[\begin{align*} 4 k T R \cdot \frac{1}{2 \pi RC} \cdot \frac{\pi}{2} = \frac{k T}{C} \end{align*}\]
the additional factor \(\frac{\pi}{2}\) for equivalent noise bandwidth.
$\square$
Example 02
![example-01]() Example 02
Example 02
Use T model for the nmos, we can find the transfer function
\[\frac{v_{out}}{i_{n}} = \frac{R}{2}\]
 Example 01
Example 01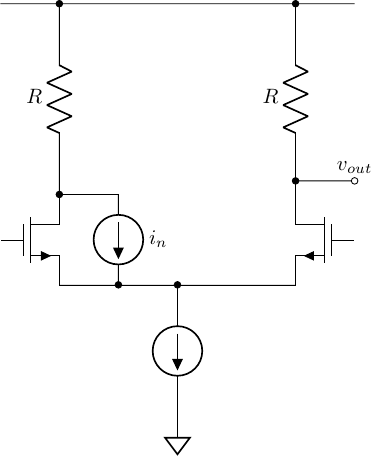 Example 02
Example 02