From Lectures by Prof. Ali Hajimiri.
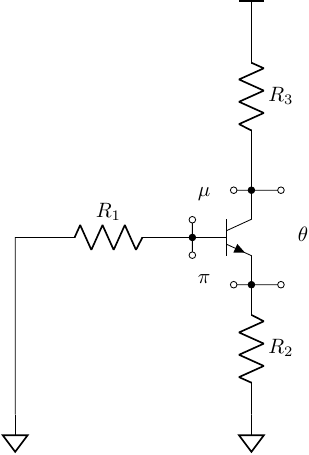
Example 01
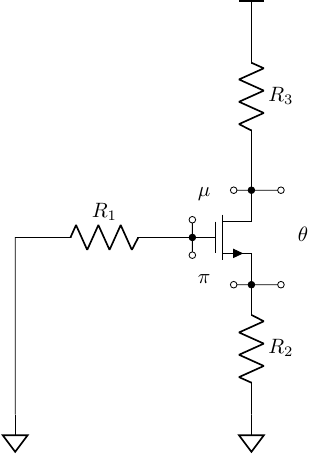 Example 01
Example 01
Solution
\[\begin{align} R_{\pi} &= \frac{R_1 + R_2}{1+g_m R_2}\\ R_{\mu} &= R_1 + R_3 + G_m R_1 R_3\\ G_m &= \frac{g_m}{1+g_m R_2}\\ R_{\theta} &= \frac{R_2 + R_3}{1+g_m R_2} \end{align}\]Step-by-Step Solution
The resistance looking into the port \(\pi\)
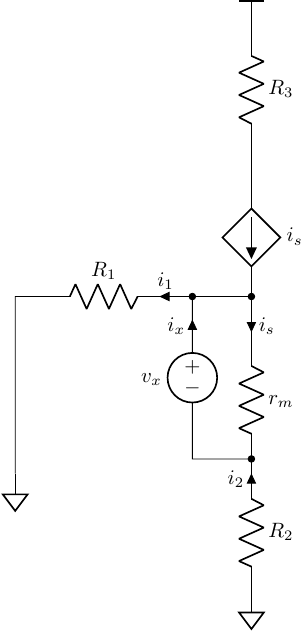 The resistance looking into the port \(\pi\)
The resistance looking into the port \(\pi\)
KCL
\[\begin{align} i_1 &= i_x\\ i_2 + i_s = i_x \quad \implies i_2 &= i_x - i_s = i_x - \frac{v_x}{r_m} \end{align}\]KVL
\[\begin{align} i_1 R_1 + i_2 R_2 = v_x \end{align}\]thus
\[\begin{align} R_{\pi} &= \frac{v_x}{i_x} = \frac{R_1 + R_2}{1+g_m R_2} \end{align}\]The resistance looking into the port \(\mu\)
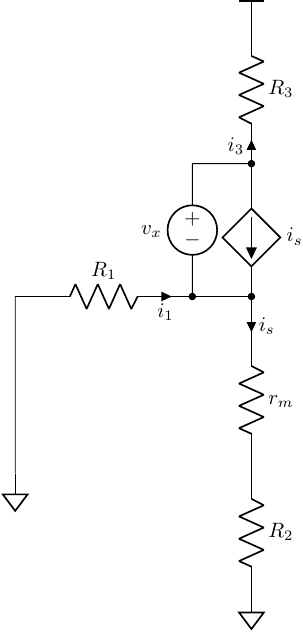 The resistance looking into the port \(\mu\)
The resistance looking into the port \(\mu\)
using
\[\begin{align} i_1 &= i_x\\ i_s (r_m + R_2) &= - i_1 R_1\\ i_3 + i_s &= i_x\\ v_x &= R_1 i_1 + R_3 i_3 \end{align}\]we got
\[\begin{align} R_{\mu} &= R_1 + R_3 + G_m R_1 R_3\\ G_m &= \frac{g_m}{1+g_m R_2} \end{align}\]The resistance looking into the port \(\theta\)
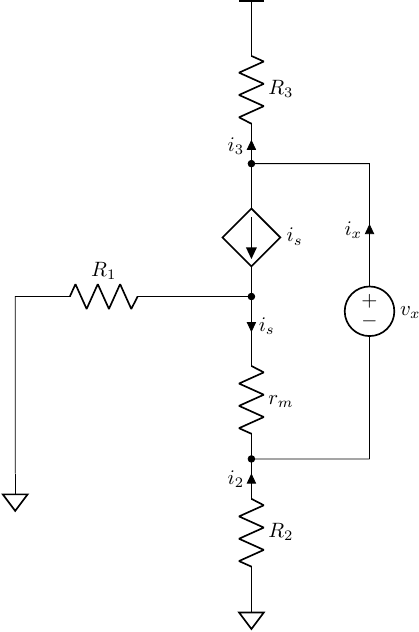 The resistance looking into the port \(\theta\)
The resistance looking into the port \(\theta\)
using
\[\begin{align} r_m i_s &= R_2 i_2\\ i_2 + i_s &= i_x\\ i_3 + i_s &= i_x\\ i_3 R_3 + i_2 R_2 &= v_x \end{align}\]we got
\[R_{\theta} = \frac{R_2 + R_3}{1+g_m R_2}\]Example 02
 Example 02
Example 02