From Robert Bogdan Staszewski Group’s Paper
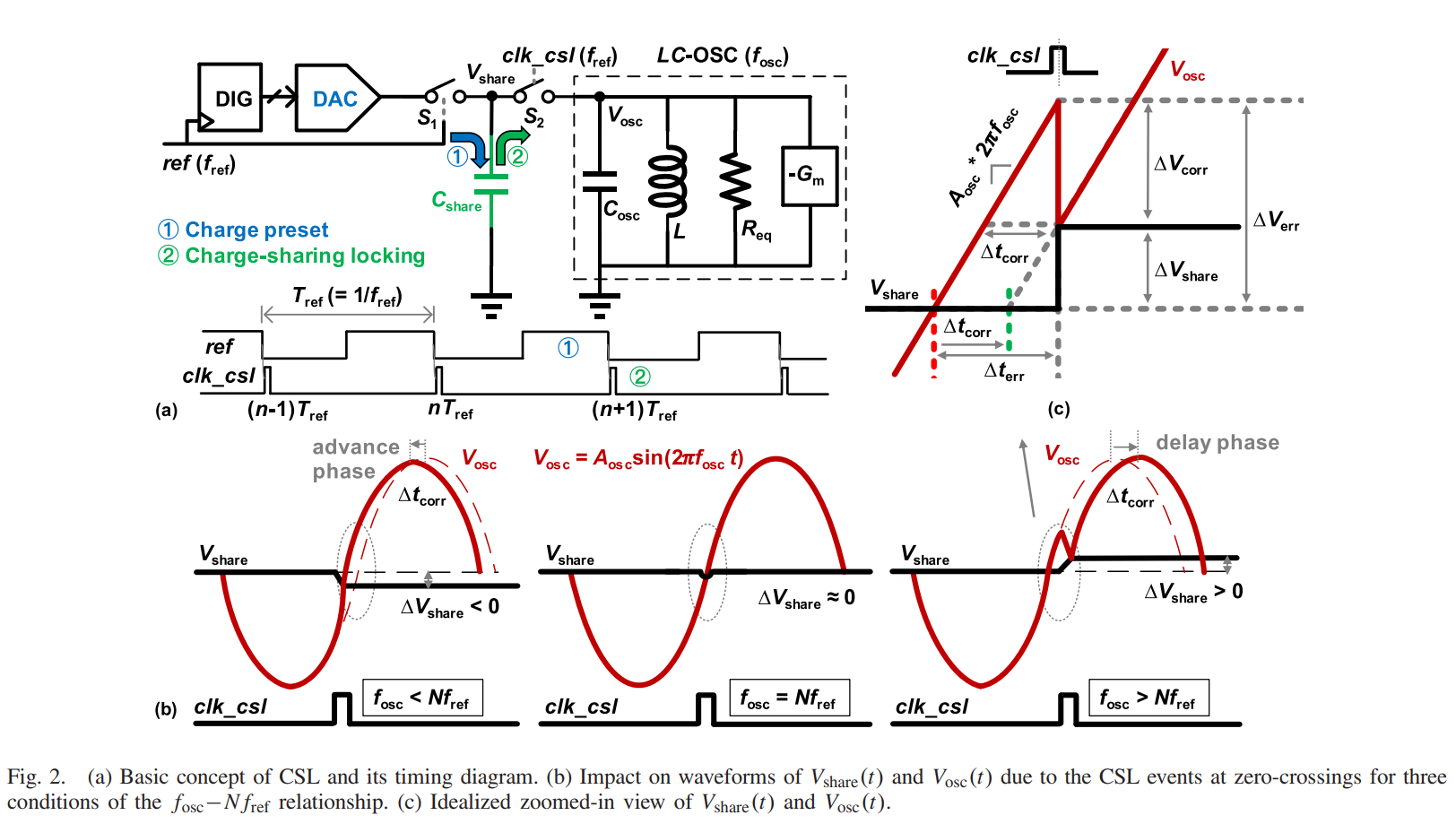
Phase Noise of Charges-Sharing Locking
Timestamps of Oscillator and Reference
\[\begin{align} t_{ref}[n] &= n T_{ref} + \Delta t_{ref}[n]\\ t_{osc}[k] &= k T_{osc} + \Delta t_{osc}[k] = \sum_{m=1}^{k}(T_{osc} + \Delta T_{osc}[m])\\ T_{ref} &= N T_{osc} \iff z_{ref}^{-1} = z_{osc}^{-N} \iff z_{osc}^{-1} = z_{ref}^{-1/N} \end{align}\]To get the spectrum from \(z\)-transform, we can substitude
\[\begin{align} z_{ref} &= e^{j2\pi \Delta f / f_{ref}}\\ z_{osc} &= e^{j2\pi \Delta f / f_{osc}} \end{align}\]Downsampling of Oscillator Timestamps
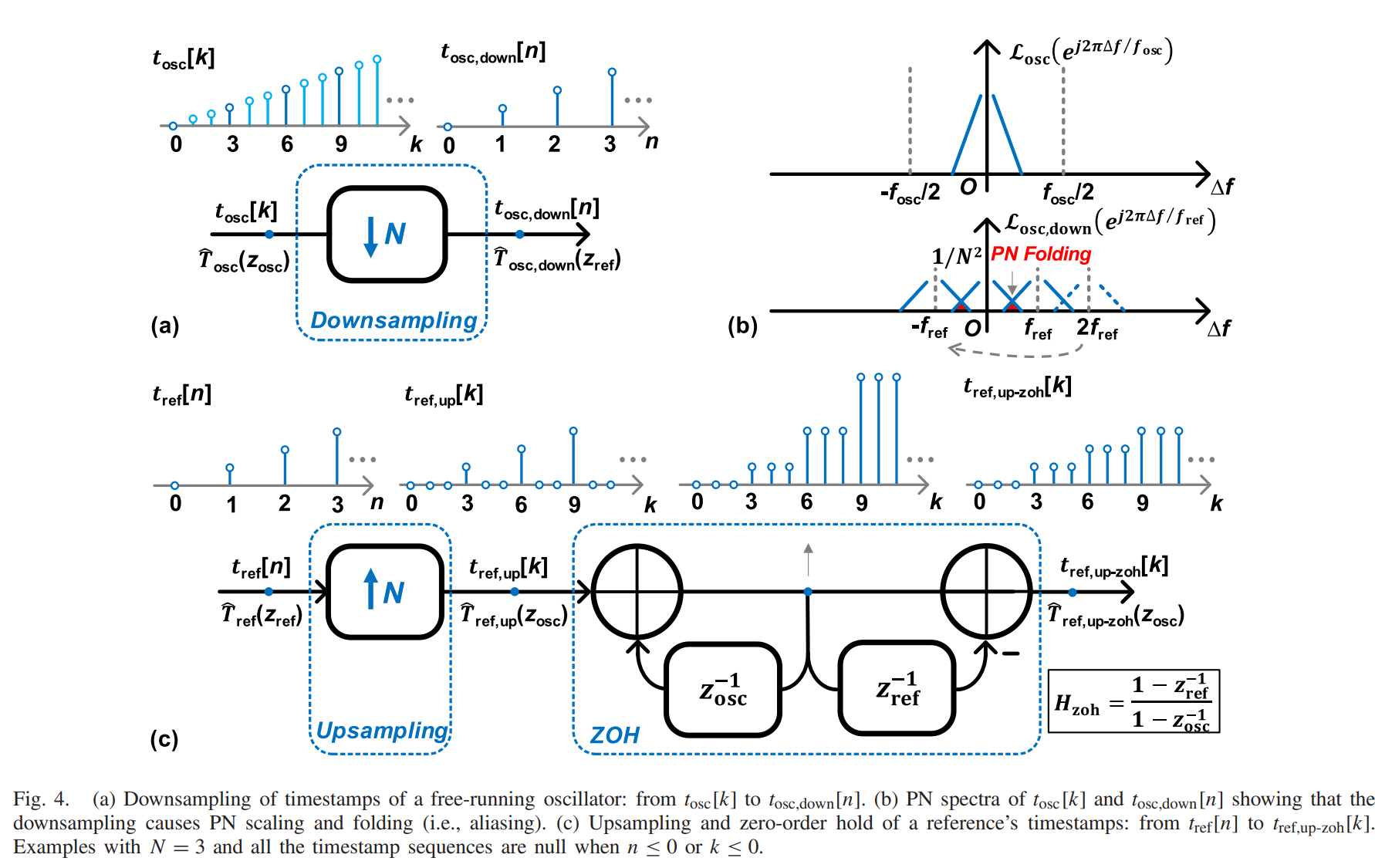
To interface a high sampling-rate (i.e., \(f_{osc}\)) domain with a low sampling-rate (i.e., \(f_{ref}\)) domain, a downsampling operation is required.1
\[\begin{align} \widehat{T}_{osc,down}(z_{ref}) &= \dfrac{1}{N} \sum_{m=0}^{N-1} \widehat{T}_{osc}(z_{ref}^{1/N} e^{-j \mspace{2mu} 2\pi \mspace{2mu} m / N})\\ &= \dfrac{1}{N} \sum_{m=0}^{N-1} \widehat{T}_{osc}(z_{osc} e^{-j \mspace{2mu} 2\pi \mspace{2mu} m / N}) \end{align}\]The PN of \(t_{osc,down}[n]\) can be calculated by taking the square of \(\vert \widehat{T}_{osc,down} \vert\) and normalizing it into phase down as2
\[\begin{align} \mathcal{L}_{osc,down}(z_{ref}) &= \dfrac{1}{N^2} \sum_{m=0}^{N-1} \mathcal{L}_{osc} (z_{osc} \mspace{1mu} e^{-j \mspace{2mu} 2\pi \mspace{2mu} m f_{ref}/f_{osc}})\\ \mathcal{L}_{osc,down}(\Delta f) &= \dfrac{1}{N^2} \sum_{m=0}^{N-1} \mathcal{L}_{osc}(\Delta f - m f_{ref}) \end{align}\]Oscillator PN \(\mathcal{L}_{osc} (z_{osc})\) can be modeled as
\[\begin{align} \mathcal{L}_{osc} (z_{osc}) &= \dfrac{(2\pi \sigma_{\Delta T,osc} / T_{osc})^2}{f_{osc}} \cdot \Big\vert \dfrac{1}{1-z_{osc}^{-1}} \Big\vert^2\\ \mathcal{L}_{osc} (\Delta f) &= \dfrac{(2\pi \sigma_{\Delta T,osc} / T_{osc})^2}{f_{osc}} \cdot \Big\vert \dfrac{1}{1-z_{osc}^{-1}} \Big\vert^2 \end{align}\]where \(\sigma_{\Delta T, osc}\) is the rms value of \(\Delta T_{osc[k]}\), the instantaneous period jitter of the oscillator. For example, \(\sigma_{\Delta T,osc} = 1 \mathrm{fs}, f_{osc} = 10 \, \mathrm{GHz}\) gives \(\mathcal{L}_{osc}\) being \(-140 \, \mathrm{dBc/Hz}\) at \(\Delta f = 10 \, \mathrm{MHz}\).

Upsampling and ZOH of Reference Timestamps
\[\begin{align} \widehat{T}_{ref,up-zoh}(z_{osc}) &= \dfrac{1-z_{ref}^{-1}}{1-z_{osc}^{-1}} \cdot \widehat{T}_{ref} (z_{ref})\\ \mathcal{L}_{ref,up-zoh}(\Delta f) &= \Big\vert \dfrac{1-z_{osc}^{-N}}{1-z_{osc}^{-1}} \Big\vert^2 \cdot \mathcal{L}_{ref}(\Delta f) \end{align}\]Neglecting the flicker PN, the reference’s instaneous absolute jitter, \(\Delta t_{ref}[n]\), is normally distributed with zero-mean and standard deviation of \(\sigma_{\Delta t,ref}\) (i.e., its rms jitter and the rms value of \(\Delta t_{ref}[n]\)). Thus, the reference’s PN could be modeled by the PSD of the Gaussian noise as
\[\mathcal{L}_{ref}(\Delta f) = \dfrac{(2\pi \sigma_{\Delta t,ref}/T_{ref})^2}{f_{ref}}\]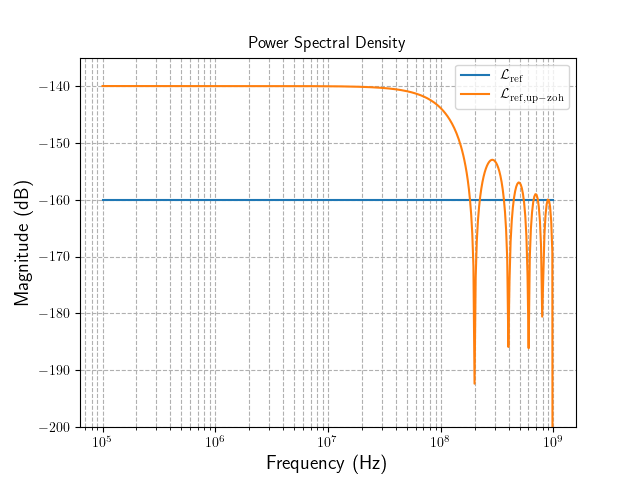
Frequency- and Phase-Controlled Oscillators

Multirate Timestamp Model of CSL (or ILO)
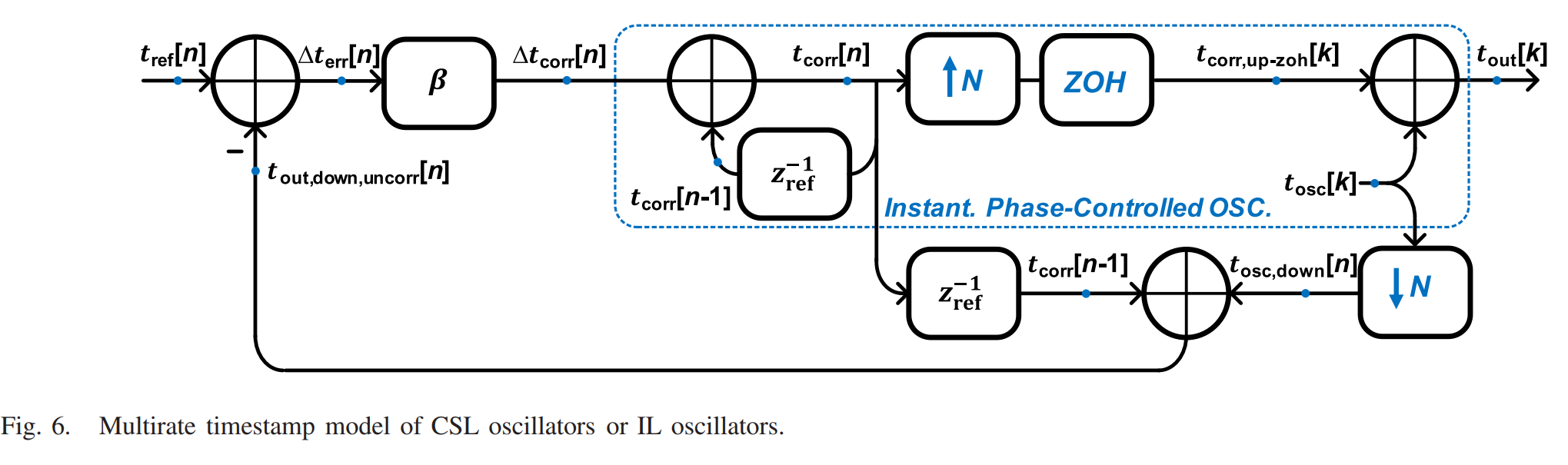
At the reference detector side
\[\beta(t_{ref}[n] - t_{out,down,uncorr}[n]) = \Delta t_{corr}[n] = t_{corr}[n] - t_{corr}[n-1]\] \[\beta (\widehat{T}_{ref} (z_{ref}) - z_{ref}^{-1} \, \widehat{T}_{corr} (z_{ref}) - \widehat{T}_{osc,down} (z_{ref})) = \widehat{T}_{corr} (z_{ref}) - z_{ref}^{-1} \, \widehat{T}_{corr} (z_{ref})\] \[\begin{equation*} \widehat {T}_{\text {corr}}(z_{\text {ref}})= \frac {\beta \left ({\widehat {T}_{\text {ref}}(z_{\text {ref}})-\widehat {T}_{\text {osc,down}}(z_{\text {ref}})}\right)}{1-(1-\beta)z_{\text {ref}}^{-1}}. \tag{28}\end{equation*}\]where
\[\begin{align} \widehat{T}_{osc,down}(z_{ref}) &= \dfrac{1}{N} \sum_{m=0}^{N-1} \widehat{T}_{osc}(z_{osc}\, e^{-j \mspace{2mu} 2\pi \mspace{2mu} m f_{ref}/f_{osc}}) \end{align}\]At the oscillator output side
\[\begin{equation*} t_{\text {out}}[k] = t_{\text {corr,up-zoh}}[k] + t_{\text {osc}}[k] \tag{29}\end{equation*}\] \[\begin{align} \widehat{T}_{out} (z_{osc}) =& \dfrac {1-z_{ref}^{-1}} {1- z_{osc}^{-1}} \cdot \widehat{T}_{corr} (z_{ref}) + \widehat{T}_{osc}(z_{osc})\\ =& \dfrac {1-z_{ref}^{-1}} {1- z_{osc}^{-1}} \cdot \dfrac{\beta}{1-(1-\beta)z_{ref}^{-1}} \bigg( \widehat{T}_{ref}(z_{ref}) - \widehat{T}_{osc,down}(z_{ref}) \bigg) + \widehat{T}_{osc}(z_{osc})\\ \widehat{T}_{out} (z_{osc}) =& \dfrac {1-z_{ref}^{-1}} {1- z_{osc}^{-1}} \cdot \dfrac{\beta}{1-(1-\beta)z_{ref}^{-1}} \cdot \widehat{T}_{ref}(z_{ref})\\ & + \bigg( 1 - \dfrac{1}{N} \dfrac {1-z_{ref}^{-1}} {1- z_{osc}^{-1}} \cdot \dfrac{\beta}{1-(1-\beta)z_{ref}^{-1}} \bigg) \cdot \widehat{T}_{osc} (z_{osc})\\ & - \dfrac{1}{N} \dfrac {1-z_{ref}^{-1}} {1- z_{osc}^{-1}} \cdot \dfrac{\beta}{1-(1-\beta)z_{ref}^{-1}} \sum_{m=1}^{N-1} \widehat{T}_{osc}(z_{osc}\, e^{-j \mspace{2mu} 2\pi \mspace{2mu} m f_{ref}/f_{osc}}) \end{align}\]the phase noise
\[\begin{align*}&\hspace {-23pt}\mathcal {L}_{\text {out}}(z_{\text {osc}}) = \left |{\frac {1}{N}\frac {1-z_{\text {ref}}^{-1}}{1-z_{\text {osc}}^{-1}}\frac {\beta }{1-(1-\beta)z_{\text {ref}}^{-1}}}\right |^{2}~N^{2} \mathcal {L}_{\text {ref}}(z_{\text {ref}}) \\&\hspace {-20pt}+\left |{1\!-\!\frac {1}{N}\frac {1\!-\!z_{\text {ref}}^{-1}}{1-z_{\text {osc}}^{-1}}\frac {\beta }{1\!-\!(1\!-\!\beta)z_{\text {ref}}^{-1}}}\right |^{2}\mathcal {L}_{\text {osc}}(z_{\text {osc}}) \\&\hspace {-20pt}+\left |{\frac {1}{N}\frac {1\!-\!z_{\text {ref}}^{-1}}{1\!-\!z_{\text {osc}}^{-1}}\frac {\beta }{1\!-\!(1\!-\!\beta)z_{\text {ref}}^{-1}}}\right |^{2}\sum _{m=1}^{N-1}\mathcal {L}_{\text {osc}}(z_{\text {osc}}e^{-j2\pi mf_{\text {ref}}/f_{\text {osc}}}) \tag{22}\end{align*}\]Assuming \(\mathcal{L}_{ref} = 0\)
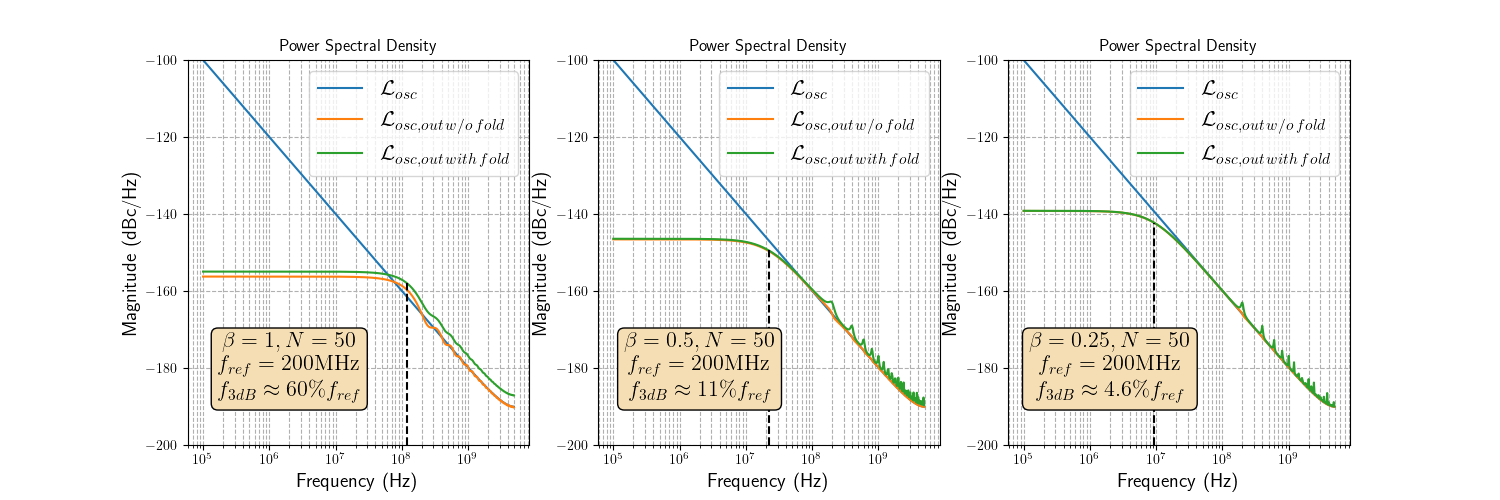
Assuming \(\mathcal{L}_{osc} = 0\)
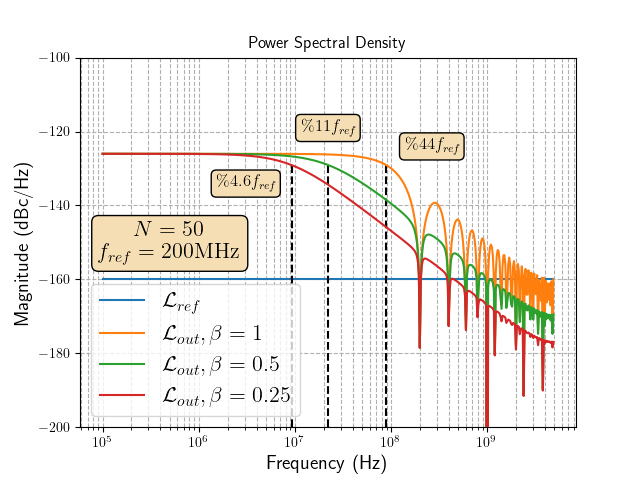
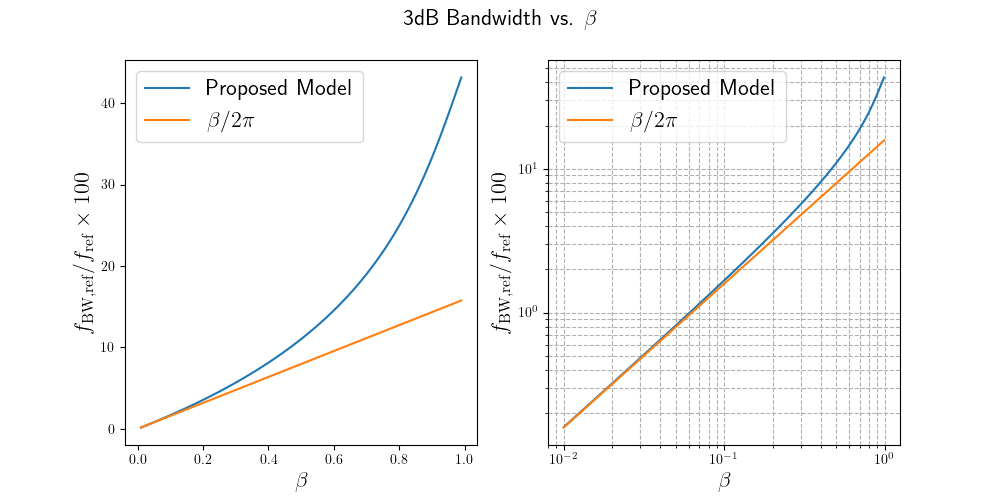
Total output jitter
\[\sigma_{out} = T_{sample} \sqrt{\dfrac{1}{2\pi^2} \int_{0}^{f_{sample}/2} \mathcal{L}_{out}(f) df}\]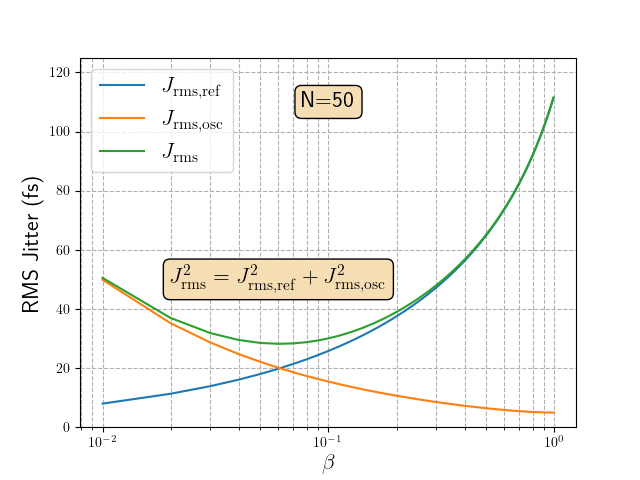
Footnote
The downsampling operation could model the edge removal or frequency division in divider-based Plls, a sub-sampling operation in divider-less PLLs (e.g., ADPLLs or SS-PLLs), and CSL/IL. Intrinsically, there should be no fundamental difference between the divider-based PLLs or divider-less PLLs. ↩
The corss products of two \(\widehat{T}_{osc}\) at different harmonics of \(f_{ref}\) could be practically neglected as compared to the self-squares. ↩