From Robert A. Wannamaker’s Paper
1. Introduction
A. The Classical Model of Quantization
For Mid-tread quantization
\[Q(w) = \Delta \lfloor \frac{w}{\Delta} + \frac{1}{2} \rfloor\]where $\lfloor . \rfloor$ is floor function, e.g.,
\[\begin{align} \lfloor 0.5 \rfloor &= 0\\ \lfloor 1 \rfloor &= 1\\ \lfloor 1.5 \rfloor &= 1 \end{align}\]B. Dither: Subtractive versus Nonsubtractive
For SD (subtractively diththered), total error is
\[\varepsilon = q(x+\nu)\]For nonsubstractively dithered system
\[\varepsilon = q(x+\nu) + \nu\]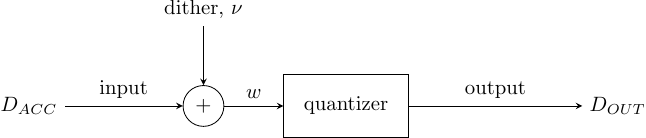 Nonsubtractively dither
Nonsubtractively dither
define total error
\[\varepsilon \overset{\triangle}{=} output - input = D_{OUT} - D_{ACC}\]It has been shown by Schuchman that
Nonsubtractive Dither Theory
A. Total Error PDF’s
The input to the quantizer is \(w=x+\nu\), which is the sum of the system input and the statistically independent dither process. This sum has a cpdf \(p_{w|x}(w,x) = p_{\nu}(w-x)\). If the quantizer outputs \(k\Delta\), the total error is \(k\Delta - x\)
\[p_{\varepsilon|x}(\varepsilon,x) = \sum_{k=-\infty}^{\infty} \delta(\varepsilon + x - k\Delta) \int_{-\frac{\Delta}{2} + k\Delta}^{\frac{\Delta}{2} + k\Delta} p_{\nu}(w-x)dw\]given \(\varepsilon\) and \(x\), there is at most one \(k\) such that \(\delta(\varepsilon + x - k \Delta)\) is not zero. Writing the integral in the last equation as a convolution (which is denoted by \(*\)) of \(p_{\nu}\) with a rectangular window function \(\Delta \Pi_{\Delta}\) reduces it to
\[p_{\varepsilon|x}(\varepsilon,x) = [\Delta \Pi_{\Delta} * p_{\nu}](\varepsilon)W_{\Delta}(\varepsilon + x)\]where
\[W_{\Gamma}(\varepsilon) \overset{\triangle}{=} \sum_{k=-\infty}^{\infty} \delta(\varepsilon - k\Gamma)\]Thus, the pdf of \(\varepsilon\) is given by (since \(W_{\Delta}(\varepsilon)\) is even function)
\[\begin{align} p_{\varepsilon}(\varepsilon) &= \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} p_{\varepsilon|x}(\varepsilon,x) p_x(x)dx\\ &= [\Delta\Pi_{\Delta} * p_{\nu}](\varepsilon) [W_{\Delta} * p_x](-\varepsilon) \end{align}\]Theorem:
\(E[\varepsilon^m]\) is independent of the distribution of the input \(D_{ACC}\) if and only if
\[\frac{\partial^m}{\partial u^m}[\mathrm{sinc}(u) \cdot \mathcal{F}[p_{\nu}](u)] \bigg|_{u=k} = 0\]for all integer \(k\) with exception of 0. Where
\[\begin{align*} \mathrm{sinc}(u) &= \frac{\sin(\pi u)}{\pi u}\\ \mathcal{F}[p_{\nu}](u) &= \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} p_{\nu}(x) e^{-j2\pi u x} dx \end{align*}\]